
How is lung ultrasound performed in children and infants and what are its uses?

Chest ultrasound, especially lung ultrasound, has been used for decades to diagnose diseases in infants and children. Inflammation and infection of the lung tissue can cause lung problems. The entry of viral, bacterial, fungal or parasitic agents into the lungs can cause infection. A lung infection is called pneumonia.
Pneumonia is very dangerous for infants and children and its diagnosis is considered as an emergency measure. There are several imaging modalities for identifying pneumonia. Most imaging techniques, including X-rays and CT scans, use X-rays to create images of the inside of the body.
Most imaging techniques, including X-rays and CT scans, use X-rays to create images of the inside of the body. Therefore, its use is dangerous for infants and children of growing age. The main concern about X-rays is the increased risk of the child developing cancer.
On the other hand, in order to perform radiographic examinations and CT scans in infants and children, they should be transferred to the radiology department. Transfer to the radiology department and use of anesthesia for imaging prolongs the diagnosis and delays treatment.
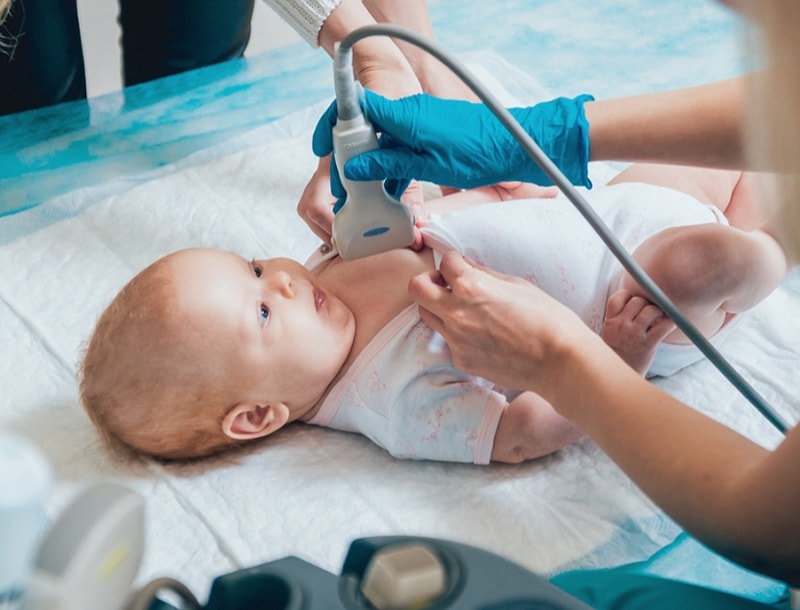
In urgent and special cases, the use of chest ultrasound instead of radiography and CT scan is recommended. Ultrasound uses ultrasound for imaging, which is completely harmless. To perform a lung ultrasound (LUS), the radiologist dips the baby or child’s chest into the ultrasound gel and places an ultrasound probe on it. Images are displayed simultaneously on the monitor. Lung ultrasound usually takes between 10 minutes and half an hour.
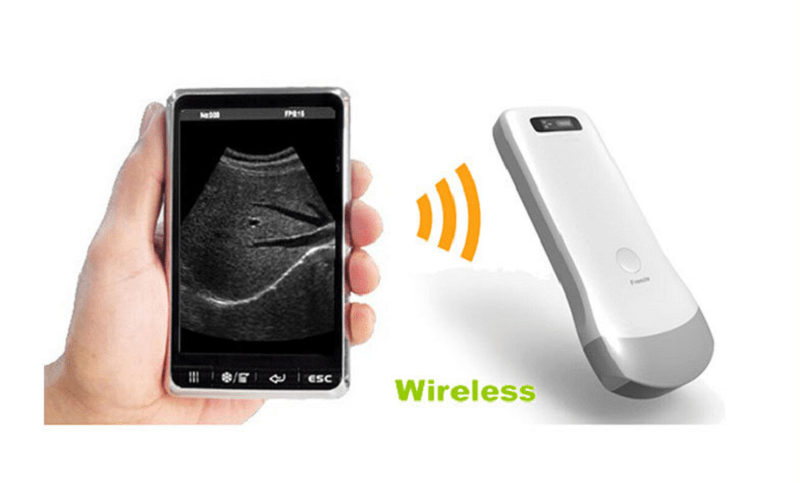
The use of hand-held portable ultrasound devices can be a great help in diagnosing lung problems in infants and children.
What organs is used for chest ultrasound?
Thymus can be well evaluated with chest ultrasound. The thymus is a pyramidal gland located in the back and upper part of the sternum. Ultrasound is also able to examine the mediastinum. The mediastinum is the central cavity of the chest that is bounded on the front by the sternum, on the back by the spine, and on both sides by the lungs.
Evaluation of pleural effusion (fluid accumulation in the lungs), dense lung masses (consolidation), diaphragmatic movements, and sometimes adult and pediatric tumors is also possible with ultrasound. Over time, more capabilities such as assessing the chest wall have been added to ultrasound applications. Examination of the chest wall can detect rib abnormalities, sternal fractures, and musculoskeletal disorders. Ultrasound of soft tissue masses of the chest, such as the breasts, lymph nodes, and vascular malformations, has also recently been added to ultrasound applications.
Ultrasound can be used to diagnose embolism or thrombosis due to catheterization in the thoracic arteries. Non-bony parts of infants can be examined by ultrasound. Lung ultrasound is performed based on the analysis of echogenic ultrasound waves and the differentiation of the resulting artifacts. Today, various lung ultrasound artifacts are very important and effective in assessing lung condition. Interpretation of ultrasound images of various lung pathologies is mainly achieved by measuring the ratio of gas to fluid in the lung parenchymal tissue and interstitial tissues.
Numerous phenomena have been described in lung ultrasound. Various new terms and symbols, including lines A and B, seashore marks, sliding marks, bat marks, and trailing artifacts, are well-known lung ultrasound terms.
Lung ultrasound and its application in the diagnosis of diseases in children and infants
Lung ultrasound has expanded as a support tool for emergency patients. The use of lung ultrasound in routine examinations has gone through several stages over the past 50 years. Some of the first papers to show the potential of lung ultrasound in the diagnosis of pneumonia were published in the 1970s. Early papers study the chest in all its components, from the mediastinum to the diaphragm.
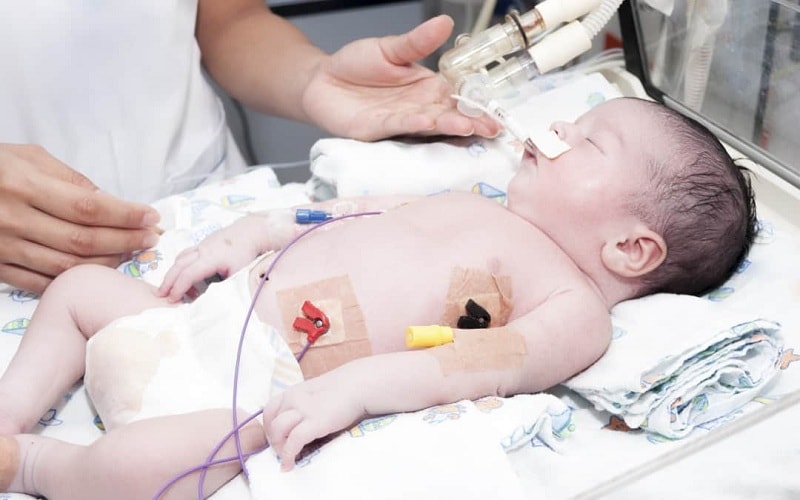
According to the Italian article by Paolo Toma, in the second half of the 1980s, Avni and her colleagues were the first to diagnose hyaline membrane disease with lung ultrasound.(مؤنث) In general, 50% of infant mortality occurs due to hyaline membrane disease or Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS). Lung ultrasound can detect congenital lung abnormalities. Lung ultrasound with a wide range of diagnostic models for hyaline membrane diseases, neonatal tachypnea (rapid breathing), meconium aspiration syndrome (fetal fecal entry into the lungs), neonatal pneumonia, pneumothorax (accumulation of air in the peripheral space and obstruction of the lungs) and Bronchopulmonary dysplasia has become a useful tool in neonatal intensive care unit.
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia is a chronic lung disease. Premature babies or babies born prematurely are often at risk for bronchopulmonary dysplasia. This disease is dangerous and requires special medical care. However, many babies who get it recover completely. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia is often associated with respiratory distress syndrome, which leads to inflammation and ulceration of the lungs.
In 2007, Copetti and Catararossi described the ultrasound pattern of infant tachypnea. In the same year, the ultrasound pattern of Respiratory Distress Syndrome was published. The most common lung disorder in newborns is tachypnea. The lung symptoms of infants in such conditions are very sensitive. At the initial ultrasound of all infants, B-lines are seen in the lower lungs. However, these lines appear uncompressed in the upper half of the lung. More whiteness in the images indicates changes at the level of the lungs.
The authors emphasize the detection of irregularity of the pleural line and consider it as a feature of respiratory distress syndrome. However, chest radiographs are still necessary to look at the chest, lines, tubes, wires, and air leakage phenomena. This has led to the integration of chest radiographswith ultrasound images. In addition, diagnosing pneumothorax on lung ultrasound as a emphysema (loss of lung elasticity) is a challenging diagnosis.
NICU The role of portable ultrasound devices in the neonatal ward
Imaging techniques are not always available. This challenge has led to the development of portable ultrasound devices. Lung ultrasound as a diagnostic method for special conditions such as the diagnosis of pneumonia in infants and children is a good alternative to chest radiography. In general, lung ultrasound has been developed to diagnose pediatric diseases. This is especially true in the diagnosis of pneumothorax.
Recent studies have shown the use and findings of lung ultrasound in neonatal respiratory distress syndrome, unstable tachypnea (rapid breathing) in infants (TTN, or wet lung’s old term), and other lung diseases. In addition, LUS is used to find small dense masses in the margins of the lungs, to image small pulmonary effusions, and even to diagnose pneumothorax in infants.
Diagnosing tachypnoea in premature or full-term infants remains a challenge for physicians. Because tachypnea does not have a specific diagnosis and is a differential diagnosis. So there are a lot of challenges to the accuracy of new imaging options that allow for fast differentiation. In the meantime, the baby’s symptoms and clinical information can help make a more accurate diagnosis.
Unfortunately, there are very few studies comparing lung ultrasound with standard CT scans. In general, lung ultrasound is less sensitive than other imaging modalities in the differential diagnosis of lung disease. However, the use of LUS has been developed to rapidly diagnose neonatal diseases in the NICU neonatal intensive care unit and the pediatric ward.
For consultation and purchase of lightweight and portable portable ultrasound devices (hand-held), you can contact the experts of Vitrin Mod website at 02188173401.
What is pneumothorax and how is it diagnosed by lung ultrasound?
As a result of the penetration of open air between the two adjacent layers (thin membranes of the lungs), part or all of the lungs become overlapped, which is called pneumothorax. Of course, its correct pronunciation is nomothorax. Shortness of breath and chest pain are common symptoms of pneumothorax.
Ultrasound is performed to diagnose pneumothorax in an emergency. The most important ultrasound criterion for the diagnosis of pneumothorax; Failure to see the lateral parts of the lung, which is about 95% sensitive. However, lung breathing movements may not be seen in patients with severe swelling such as asthma, extracorporeal aspiration, or emphysema.
Studies have shown that the diagnosis of pneumothorax depends on the experience of the ultrasound machine operator. Lung ultrasound is a three-dimensional technique that covers about 70% of the surface of the lung. Unfortunately, lung ultrasound is not able to scan the central airways and is not able to assess the hila’s membrane and lesions that are far from the pleura. Hila is a compact, triangular area that allows the bronchi, blood vessels, and nerves to enter the lungs.
Lung ultrasound can add information to chest radiography and complement clinical approaches. Unfortunately, there are limited studies in this area. Less than 10% of the articles on lung ultrasound have been published in radiology journals in the last 10 years.


2 comments